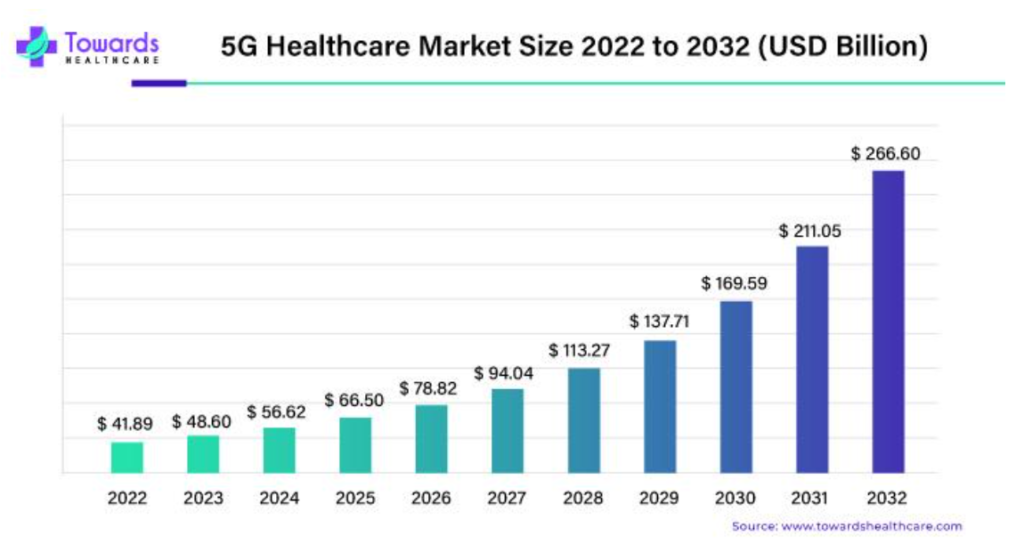
The global 5G healthcare market is poised for unprecedented growth, projected to escalate from a valuation of USD 41.89 billion in 2022 to a staggering USD 266.60 billion by the year 2032. This impressive surge signifies a substantial CAGR of 20.82% between the years 2023 and 2032. This profound evolution is a direct consequence of the burgeoning demand for patient-centered care and the accelerating adoption of remote surgeries.
The intersection of healthcare and technology has always been a fertile ground for innovation, and the advent of 5G technology promises to revolutionize the way we deliver and receive medical care. With its lightning-fast speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive connectivity, 5G is poised to unlock a myriad of opportunities for the healthcare industry, paving the way for more efficient, accessible, and patient-centered care.
One of the key drivers behind the adoption of 5G in healthcare is its ability to support remote patient monitoring and telehealth services. With 5G’s high-speed data transmission capabilities, healthcare providers can remotely monitor patients’ vital signs in real-time, enabling early intervention and proactive management of chronic conditions. Moreover, teleconsultations powered by 5G offer patients greater convenience and accessibility, with studies showing that a significant portion of millennials prefer online consultations over in-person visits.
Big data analytics is another area where 5G is poised to make a substantial impact. The healthcare industry is experiencing an exponential increase in the volume of data generated, thanks to advancements in technology and the widespread adoption of electronic health records. 5G technology facilitates faster and more efficient analysis of this data, enabling healthcare providers to glean valuable insights that can inform personalized treatment plans and improve patient outcomes.
Recent advancements in robotics have enabled the practice of surgery remotely, a technique known as robotic telesurgery. In this method, a skilled surgeon can operate from a different location than the patient, using tools to direct a robotic system performing the surgery. The surgeon receives visual feedback through a screen or VR glasses, along with audible cues.
While remote surgery has shown promise, it faces challenges such as high transmission latency and overhead. Latency issues can lead to unsynchronized feedback, where visual, auditory, and haptic cues arrive at different rates. The emergence of 5G networks, with latency as low as 1-2 milliseconds, holds the potential to revolutionize remote surgery by offering dependable and ultra-fast connections. Already, 5G technology has facilitated successful remote surgeries, including spinal and endoscopic procedures.
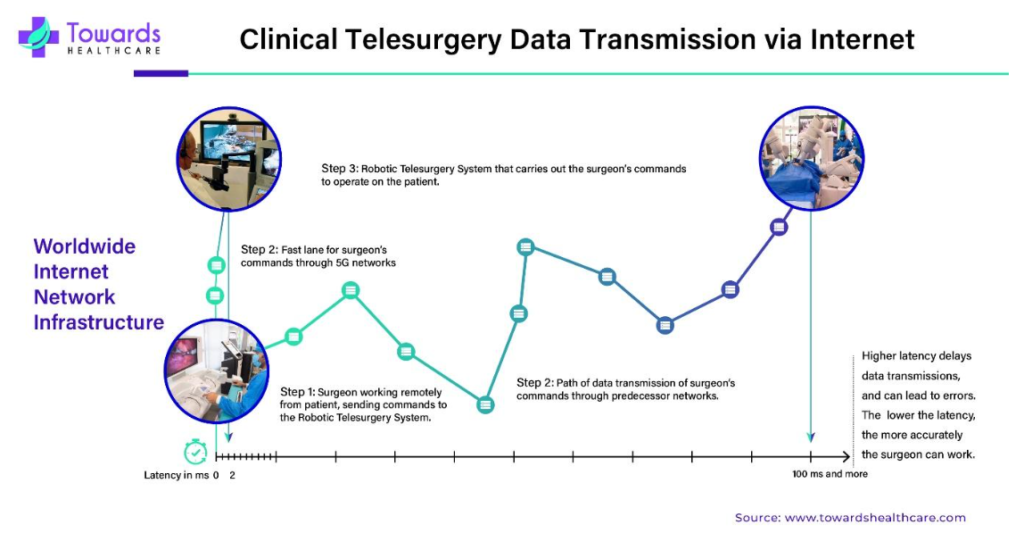
5G networks could enhance telemetered surgery, where surgeons with specialized expertise guide procedures remotely via video links. This approach could also extend to 5G-enabled ambulances, where medical professionals provide real-time guidance to ambulance crews caring for patients. For instance, in May 2020, the University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust and British Telecom conducted the UK’s first remote diagnostic process using a 5G-connected ambulance, showcasing the transformative potential of such technologies in improving patient care.
In the robotic surgery, significant strides have been made, particularly in fields such as urology, gynecology, thoracic, cardiothoracic, and gastrointestinal surgeries. Robotic-assisted procedures, like radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer, have become increasingly common, revolutionizing surgical care. The adoption of robotic surgery has seen a remarkable rise in hospitals worldwide, with Michigan hospitals alone witnessing an 8.4-fold increase in robotic surgery utilization over six years.
The rollout of 5G networks is expected to accelerate the development and adoption of innovative healthcare applications such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and extended reality (XR). These immersive technologies have the potential to revolutionize medical education, surgical training, and patient engagement, ultimately leading to better healthcare delivery.
Remote surgery, a concept once relegated to the realm of science fiction, is now becoming a reality with the advent of 5G technology. By reducing latency to as low as 1-2 milliseconds, 5G enables surgeons to perform complex procedures from remote locations with unprecedented precision and accuracy. This has profound implications for areas with limited access to specialized medical care, as it can potentially democratize access to life-saving treatments and procedures.
Geographical Landscape
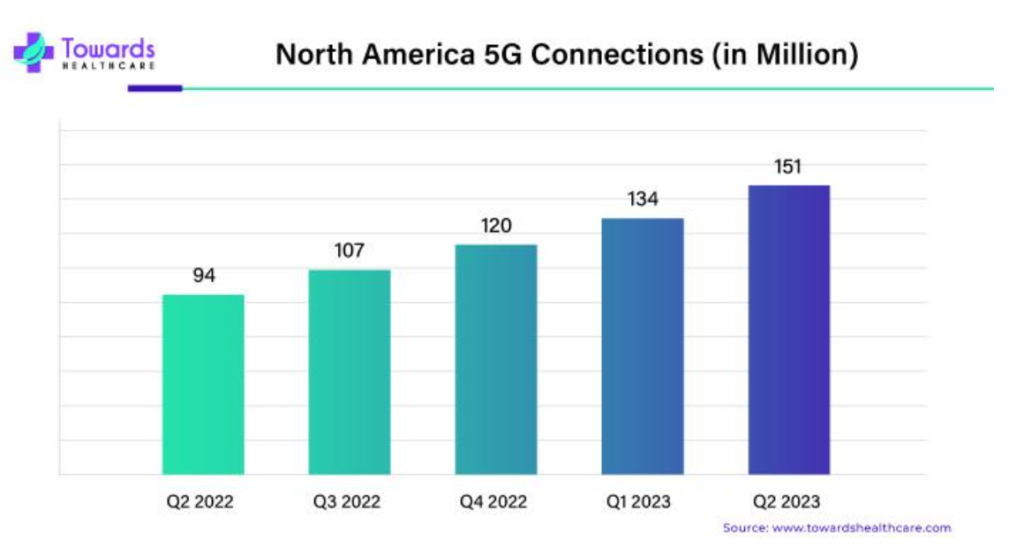
In addition to its technological advancements, the widespread adoption of 5G in healthcare is also being facilitated by supportive government regulations and investments. Regions like North America, with its advanced healthcare infrastructure and favorable regulatory environment, are leading the charge in 5G adoption. Initiatives such as AT&T’s private 5G network at USC’s Lawrence J. Ellison Institute for Transformative Medicine are showcasing the transformative potential of 5G in enhancing patient care and research capabilities.















