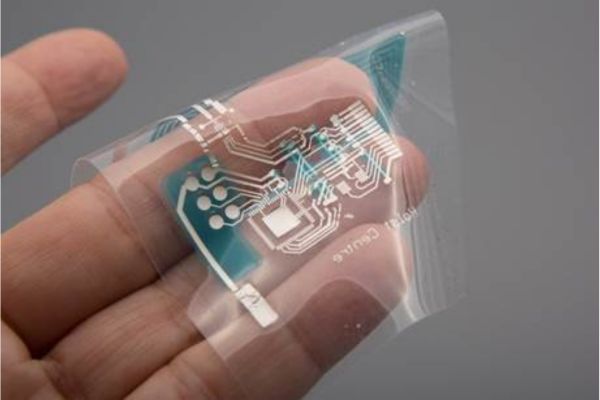
Printed electronics is a revolutionary technology that involves the printing of electronic components and circuits onto various substrates, including flexible materials like plastic, paper, and textiles. Unlike traditional electronics manufacturing methods, which typically involve etching and deposition processes on rigid substrates, printed electronics offer a more cost-effective, scalable, and versatile approach to creating electronic devices and systems.
Market Overview: The printed electronics market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for lightweight, flexible, and low-cost electronic solutions across a wide range of industries. According to research reports, the global printed electronics market is projected to reach a value of over $20 billion by 2026, with significant contributions from sectors such as consumer electronics, healthcare, automotive, and smart packaging.
Key Drivers and Trends: Several factors are driving the growth of the printed electronics market. One of the primary drivers is the rising demand for flexible and wearable electronics. Consumers are increasingly seeking devices that can conform to their bodies and lifestyles, driving the development of flexible displays, sensors, and batteries enabled by printed electronics technology.
Another key trend in the printed electronics market is the focus on sustainability and environmental friendliness. With growing concerns about electronic waste and the environmental impact of traditional electronics manufacturing processes, printed electronics offer a more sustainable alternative. By using recyclable materials and reducing energy consumption during manufacturing, printed electronics contribute to a more eco-friendly approach to electronics production.
Moreover, advancements in printing technologies and materials have expanded the capabilities of printed electronics, enabling the creation of complex electronic circuits and components with high resolution and reliability. Inkjet printing, screen printing, and additive manufacturing techniques have become increasingly sophisticated, allowing for the deposition of conductive inks, semiconductors, and dielectric materials with precision and efficiency.
Applications Across Industries: The versatility of printed electronics has led to a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Consumer Electronics: Printed electronics are revolutionizing the consumer electronics market by enabling the development of flexible displays, touch sensors, and wearable devices. From foldable smartphones to smart clothing embedded with sensors, printed electronics are driving innovation in consumer electronics design and functionality.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, printed electronics are being used to create wearable health monitors, medical sensors, and drug delivery systems. Flexible and lightweight sensors can monitor vital signs and biomarkers in real-time, enabling remote patient monitoring and personalized healthcare solutions.
- Automotive: Printed electronics are reshaping the automotive industry by enhancing vehicle safety, comfort, and connectivity. Printed sensors, antennas, and OLED displays enable advanced features such as collision avoidance systems, keyless entry, and infotainment displays, improving the driving experience and vehicle performance.
- Smart Packaging: Printed electronics are transforming traditional packaging into interactive and intelligent platforms for product authentication, tracking, and communication. Smart labels, RFID tags, and sensors integrated into packaging materials provide valuable information to consumers and supply chain stakeholders, enhancing product safety and brand engagement.
Challenges and Opportunities: While the printed electronics market holds immense promise, several challenges need to be addressed to unlock its full potential. One of the key challenges is achieving scalability and reliability in manufacturing processes. Improvements in material performance, printing resolution, and quality control are essential to ensure consistent and high-quality production of printed electronic devices.
Additionally, standardization and interoperability are critical for driving widespread adoption of printed electronics across industries. Establishing industry-wide standards for materials, processes, and performance metrics will facilitate collaboration, innovation, and market acceptance of printed electronic products and systems.